What Is Edge AI and How Does It Work?
Recent strides in the efficacy of AI, the adoption of IoT devices and the power of edge computing have come together to unlock the power of edge AI.

Countless analysts and businesses are talking about and implementing edge computing, which traces its origins to the 1990s, when content delivery networks were created to serve web and video content from edge servers deployed close to users.
Today, almost every business has job functions that can benefit from the adoption of edge AI. In fact, edge applications are driving the next wave of AI computing in ways that improve our lives at home, at work, in school and in transit.
Learn more about what edge AI is, its benefits and how it works, examples of edge AI use cases, and the relationship between edge computing and cloud computing.
What Is Edge AI?
Edge AI is the deployment of AI applications in devices throughout the physical world. It’s called “edge AI” because the AI computation is done near the user at the edge of the network, close to where the data is located, rather than centrally in a cloud computing facility or private data center.
Since the internet has global reach, the edge of the network can connote any location. It can be a retail store, factory, hospital or devices all around us, like traffic lights, autonomous machines and phones.
Edge AI: Why Now?
Organizations from every industry are looking to increase automation to improve processes, efficiency and safety.
To help them, computer programs need to recognize patterns and execute tasks repeatedly and safely. But the world is unstructured and the range of tasks that humans perform covers infinite circumstances that are impossible to fully describe in programs and rules.
Advances in edge AI have opened opportunities for machines and devices, wherever they may be, to operate with the “intelligence” of human cognition. AI-enabled smart applications learn to perform similar tasks under different circumstances, much like real life.
The efficacy of deploying AI models at the edge arises from three recent innovations.
- Maturation of neural networks: Neural networks and related AI infrastructure have finally developed to the point of allowing for generalized machine learning. Organizations are learning how to successfully train AI models and deploy them in production at the edge.
- Advances in compute infrastructure: Powerful distributed computational power is required to run AI at the edge. Recent advances in highly parallel GPUs have been adapted to execute neural networks.
- Adoption of IoT devices: The widespread adoption of the Internet of Things has fueled the explosion of big data. With the sudden ability to collect data in every aspect of a business — from industrial sensors, smart cameras, robots and more — we now have the data and devices necessary to deploy AI models at the edge. Moreover, 5G is providing IoT a boost with faster, more stable and secure connectivity.
Why Deploy AI at the Edge? What Are the Benefits of Edge AI?
Since AI algorithms are capable of understanding language, sights, sounds, smells, temperature, faces and other analog forms of unstructured information, they’re particularly useful in places occupied by end users with real-world problems. These AI applications would be impractical or even impossible to deploy in a centralized cloud or enterprise data center due to issues related to latency, bandwidth and privacy.
The benefits of edge AI include:
- Intelligence: AI applications are more powerful and flexible than conventional applications that can respond only to inputs that the programmer had anticipated. In contrast, an AI neural network is not trained how to answer a specific question, but rather how to answer a particular type of question, even if the question itself is new. Without AI, applications couldn’t possibly process infinitely diverse inputs like texts, spoken words or video.
- Real-time insights: Since edge technology analyzes data locally rather than in a faraway cloud delayed by long-distance communications, it responds to users’ needs in real time.
- Reduced cost: By bringing processing power closer to the edge, applications need less internet bandwidth, greatly reducing networking costs.
- Increased privacy: AI can analyze real-world information without ever exposing it to a human being, greatly increasing privacy for anyone whose appearance, voice, medical image or any other personal information needs to be analyzed. Edge AI further enhances privacy by containing that data locally, uploading only the analysis and insights to the cloud. Even if some of the data is uploaded for training purposes, it can be anonymized to protect user identities. By preserving privacy, edge AI simplifies the challenges associated with data regulatory compliance.
- High availability: Decentralization and offline capabilities make edge AI more robust since internet access is not required for processing data. This results in higher availability and reliability for mission-critical, production-grade AI applications.
- Persistent improvement: AI models grow increasingly accurate as they train on more data. When an edge AI application confronts data that it cannot accurately or confidently process, it typically uploads it so that the AI can retrain and learn from it. So the longer a model is in production at the edge, the more accurate the model will be.
How Does Edge AI Technology Work?
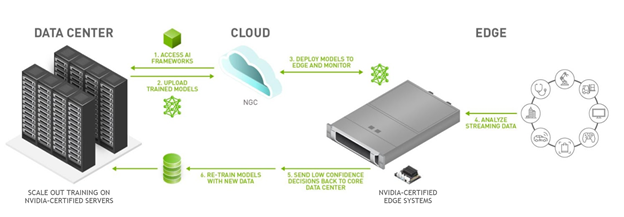
For machines to see, perform object detection, drive cars, understand speech, speak, walk or otherwise emulate human skills, they need to functionally replicate human intelligence.
AI employs a data structure called a deep neural network to replicate human cognition. These DNNs are trained to answer specific types of questions by being shown many examples of that type of question along with correct answers.
This training process, known as “deep learning,” often runs in a data center or the cloud due to the vast amount of data required to train an accurate model, and the need for data scientists to collaborate on configuring the model. After training, the model graduates to become an “inference engine” that can answer real-world questions.
In edge AI deployments, the inference engine runs on some kind of computer or device in far-flung locations such as factories, hospitals, cars, satellites and homes. When the AI stumbles on a problem, the troublesome data is commonly uploaded to the cloud for further training of the original AI model, which at some point replaces the inference engine at the edge. This feedback loop plays a significant role in boosting model performance; once edge AI models are deployed, they only get smarter and smarter.
What Are Examples of Edge AI Use Cases?
 AI is the most powerful technology force of our time. We’re now at a time where AI is revolutionizing the world’s largest industries.
AI is the most powerful technology force of our time. We’re now at a time where AI is revolutionizing the world’s largest industries.
Across manufacturing, healthcare, financial services, transportation, energy and more, edge AI is driving new business outcomes in every sector, including:
- Intelligent forecasting in energy: For critical industries such as energy, in which discontinuous supply can threaten the health and welfare of the general population, intelligent forecasting is key. Edge AI models help to combine historical data, weather patterns, grid health and other information to create complex simulations that inform more efficient generation, distribution and management of energy resources to customers.
- Predictive maintenance in manufacturing: Sensor data can be used to detect anomalies early and predict when a machine will fail. Sensors on equipment scan for flaws and alert management if a machine needs a repair so the issue can be addressed early, avoiding costly downtime.
- AI-powered instruments in healthcare: Modern medical instruments at the edge are becoming AI-enabled with devices that use ultra-low-latency streaming of surgical video to allow for minimally invasive surgeries and insights on demand.
- Smart virtual assistants in retail: Retailers are looking to improve the digital customer experience by introducing voice ordering to replace text-based searches with voice commands. With voice ordering, shoppers can easily search for items, ask for product information and place online orders using smart speakers or other intelligent mobile devices.
What Role Does Cloud Computing Play in Edge Computing?
AI applications can run in a data center like those in public clouds, or out in the field at the network’s edge, near the user. Cloud computing and edge computing each offer benefits that can be combined when deploying edge AI.
The cloud offers benefits related to infrastructure cost, scalability, high utilization, resilience from server failure, and collaboration. Edge computing offers faster response times, lower bandwidth costs and resilience from network failure.
There are several ways in which cloud computing can support an edge AI deployment:
- The cloud can run the model during its training period.
- The cloud continues to run the model as it is retrained with data that comes from the edge.
- The cloud can run AI inference engines that supplement the models in the field when high compute power is more important than response time. For example, a voice assistant might respond to its name, but send complex requests back to the cloud for parsing.
- The cloud serves up the latest versions of the AI model and application.
- The same edge AI often runs across a fleet of devices in the field with software in the cloud
Learn more about the best practices for hybrid edge architectures.
The Future of Edge AI
Thanks to the commercial maturation of neural networks, proliferation of IoT devices, advances in parallel computation and 5G, there is now robust infrastructure for generalized machine learning. This is allowing enterprises to capitalize on the colossal opportunity to bring AI into their places of business and act upon real-time insights, all while decreasing costs and increasing privacy.
We are only in the early innings of edge AI, and still the possible applications seem endless.
Latest News & Updates
Stay informed with the latest press releases, industry news, and more.







