
The AI-Ready Cable Landing Station is Coming
NJFX today announced the completion of a comprehensive Basis of Design for a new 10MW high-density AI data hall, delivering an expected 1.25 PUE and 8MW of usable IT load.

CEO
By Gil Santaliz. Originally published by Disaster Recovery Journal in May 2021.
June 1, 2021
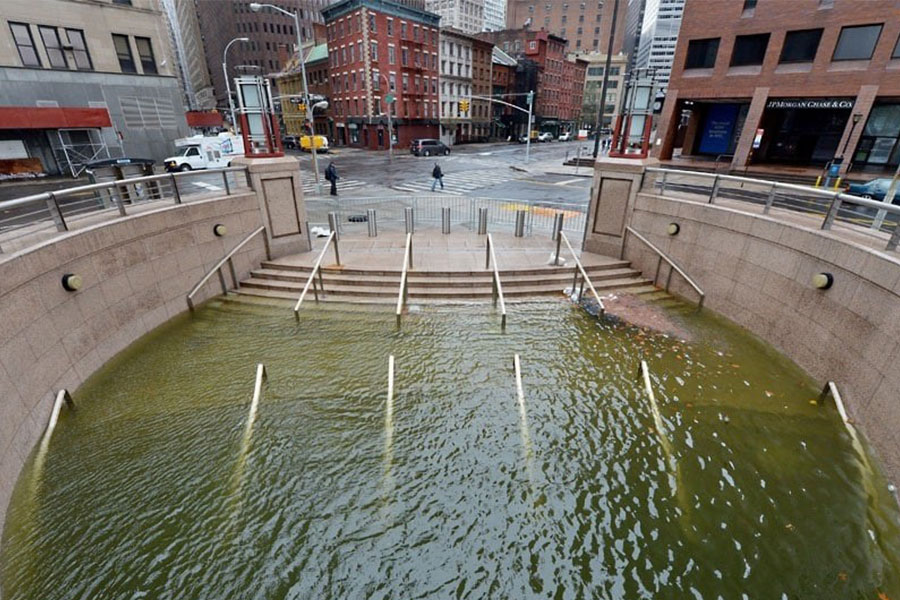

The Dawn of Communications
North American telecommunications originated in New York, with the first transatlantic cable. The first of the legacy carriers, “Ma” Bell, AT&T and others being headquartered at the source of those very first international communications, led to a centralization of communications in the better part of the last century. Even as connectivity branched out from that origination point, those legacy routes and origination points remained the same. One U.S. route that has become chronically congested and dilapidated is the Northeast Coast Corridor. Major tax incentives have led to a clustering of massive data centers in Virginia and the Carolinas. Northern Virginia alone is flush with 4.7 million square feet of commissioned data center space, according to market research from datacenterHawk. Carrier consolidation led to many long-haul networks being used for local distribution, which made record keeping impossible during the many integrations. Institutions historically engineered multiple paths but were beholden to what was offered by carriers as to routes and diversity. Telecom is as collaborative as it is competitive. Fiber providers often lease access from one another. In addition, it’s very difficult to ascertain the underground routes that these fiber links take in the last mile. In the always on, always available climate, network design must get smarter for both the steady state and when systems are disrupted. Flexibility to control and redirect the network needs to be the new norm. The ability to do so comes back to having access to hubs that can maintain connectivity, as well as offer alternate pathways.The Key Lies in Operational Independence
There are a few ways to ensure internet traffic does not come to a standstill. The first is network diversity. Sometimes, diversity and redundancy are used interchangeably. But they are completely different, and both must be in place. There may be a false sense of security, as organizations misinterpret diversity vs. redundancy. For example, a redundant system will help if one path goes down. But there may be several carriers in the same ductwork. Even if an organization buys capacity from three or four different carriers, the flow of data could still be impacted. It’s a false sense of security. There also needs to be a physically diverse path. And even if there are diverse physical routes, those routes might go through the same building at some point in the path. If the building has issues, you’re in the same situation. So the best way to handle network security is a mesh solution, where you have redundant routes, resilient routes AND physically diverse routes. In other words, a plan A, B, and C. This is considered operational independence.Expect the Unexpected
As we have seen with many natural, manmade and even biological events, preparation is key to keeping connectivity up and information flowing. For the infrastructure sector, this means plan and prepare. Consider uncertainties before they become a reality. No one could have predicted a global pandemic that stretched on for more than a year would change the way most of us live and work. At the heart of this disruption was our connectivity. If the pandemic hit just a decade ago, it would not be possible to remotely do very much of anything for an extended period of time. Increased capacity this past year put a demand on global networks, and those networks and their operators rose to the challenge. While it was certainly stretched thin, the internet did not break. One reason for this is the behind-the-scenes efforts to provide increased capacity and connectivity to organizations. In order to do this, essential workers remained on site at data centers, cable landing stations and IT departments around the world. To have that team in place, operations-based preparedness measures are critical to avoiding any and all downtime for customers. For a predictable event like a storm, those measures should include:
NJFX today announced the completion of a comprehensive Basis of Design for a new 10MW high-density AI data hall, delivering an expected 1.25 PUE and 8MW of usable IT load.

NJFX today announced the completion of a comprehensive Basis of Design for a new 10MW high-density AI data hall, delivering an expected 1.25 PUE and 8MW of usable IT load.

Red Sea conflict threatens Key Internet Cables. Maritime attacks complicate repairs on underwater cables that carry the world’s web traffic.

Red Sea conflict threatens Key Internet Cables. Maritime attacks complicate repairs on underwater cables that carry the world’s web traffic.

Red Sea conflict threatens Key Internet Cables. Maritime attacks complicate repairs on underwater cables that carry the world’s web traffic.
Red Sea conflict threatens Key Internet Cables. Maritime attacks complicate repairs on underwater cables that carry the world’s web traffic.
