Bloomberg TV: Undersea Cables at NJFX
Red Sea conflict threatens Key Internet Cables. Maritime attacks complicate repairs on underwater cables that carry the world’s web traffic.
Our wireless world depends on a few hundred fiber cables laid on the ocean floor
Original article posted at DataCenterDynamics.com
by Dan Swinhoe
August 31, 2021
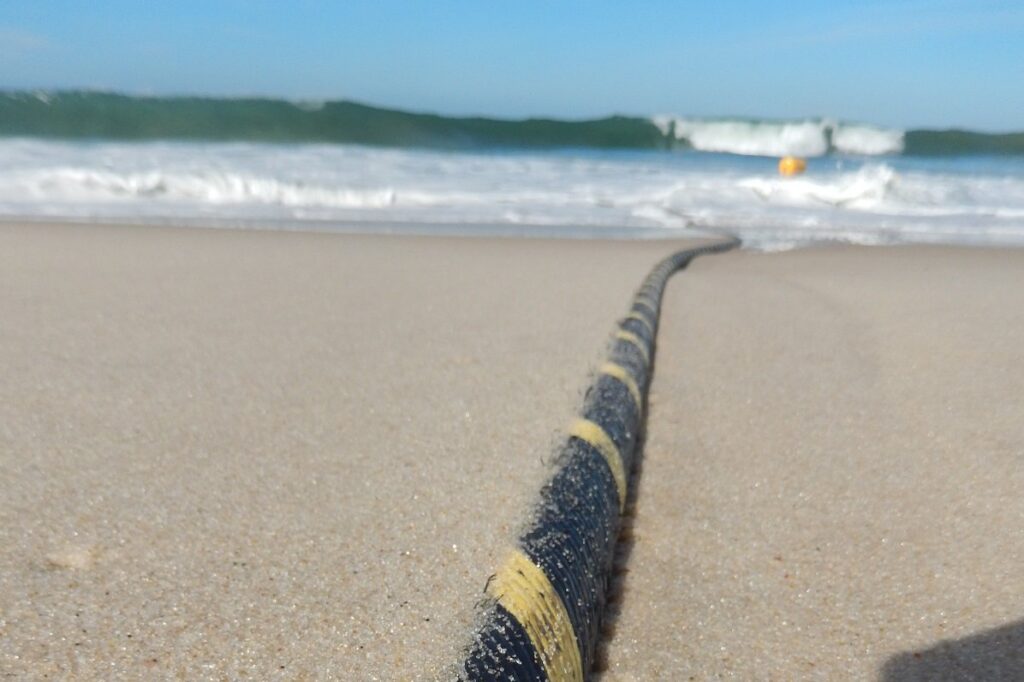

Though we live in an increasingly wireless world, that connectivity depends on wires under the ocean.
Subsea or submarine cables are fiber optic cables that connect countries across the world via cables laid on the ocean floor. These cables – often thousands of miles in length – are able to transmit huge amounts of data rapidly from one point to another.
What is a submarine cable?
A submarine cable is a fiber optic cable laid in the ocean, connecting two or more landing points.Rarely much wider than a garden hose, today cables generally comprise of the optical fibers that carry the information, which are then covered in silicon gel, then sheathed in varying layers of plastic, steel wiring, copper, and nylon in order to provide insulation to protect the signal and protect the cable from damage from wildlife, anchors & fishing, or weather & other natural events.
The cables are laid using ships that are modified specifically for this purpose, transporting and slowly laying the ‘wet plant’ infrastructure on the seabed. These special ships can carry thousands of kilometers of optical cable out to sea. A special subsea plow is also used to trough and bury submarine cables along the seabed closer to shorelines where naval activities, such as anchoring and fishing, are most prevalent and could damage submarine cables.
“We’ve had submarine cables for over 150 years,” explains Gil Santaliz, founder and CEO of New Jersey cable landing station NJFX, “and they’ve really been a way for communication between countries and continents.”“The most basic application is communicating what’s happening in one part of the world to another, but we’ve morphed that to allow applications to exist in multiple countries at the same time, to enhance the performance of applications, and to find eco-friendly locations where you can run applications with a zero-carbon footprint yet enjoy the application the country where they don’t have that resource.”
Subsea cables; connecting the world for 170 years
Work to demonstrate the potential of subsea cables began in the 1840s, when Samuel Morse, the inventor of Morse Code, submerged a wire insulated with tarred hemp and India rubber, in the water of New York Harbor and telegraphed through it in 1842.The first commercial cable was laid in 1850, when the English Channel Submarine Telegraph Company laid a telegraph cable between England and France. It was cut weeks later by fishermen thinking it was seaweed.
A successor company, the Submarine Telegraph Company, laid a second cable the next year and more cables linking the British Isles to mainland Europe followed.In 1854 and completed in 1858, the Transatlantic telegraph cable – which ran from Valentia in western Ireland to Bay of Bulls, Trinity Bay, Newfoundland and was the first to traverse the Atlantic – was laid by the Atlantic Telegraph Company. It only functioned for only three weeks before breaking beyond repair.
The first official telegram to pass between two continents – at a rate of a single character every two minutes – was a letter of congratulations from Queen Victoria of the United Kingdom to President of the United States James Buchanan on August 16. Following progressive signal deterioration, the cable was destroyed after excessive voltage was applied to try and boost the transmission strength. While it was only in operation for a short time, it showed intercontinental communication was possible and a second cable was laid in 1865.The first trans-Pacific cables were completed in 1902 and 1903, linking the US mainland to Hawaii in 1902 and Guam to the Philippines in 1903.The first subsea telephone cable, TAT-1, was laid between 1955 and 1956.
A joint project between the UK Post Office (of which BT was part for a number of years), the American Telephone and Telegraph company (now AT&T), and the Canadian Overseas Telecommunications Corporation, it was able to carry 35 simultaneous telephone calls.The eighth transatlantic communications cable, TAT-8, was the first fiber optic subsea cable. Constructed in 1988 by a consortium of companies led by AT&T, France Télécom, and British Telecom, the cable was able to carry 280 Mbits per second. It was retired in 2002.Today there are more than 400 subsea cables in operation.
Some connecting nearby islands can be shorter than 50 miles long. Others, traversing the pacific, can reach more than 10,000 miles in length. Some connect singles points across a body of water, others have multiple landing points connecting multiple countries.Antarctica is the only continent not yet reached by a submarine telecommunications cable, though one is reportedly being considered to improve connectivity for researchers in the region.Cable technology evolves quicklyAfter choosing the desired route…
Read the complete article here.###

Red Sea conflict threatens Key Internet Cables. Maritime attacks complicate repairs on underwater cables that carry the world’s web traffic.

Red Sea conflict threatens Key Internet Cables. Maritime attacks complicate repairs on underwater cables that carry the world’s web traffic.

Red Sea conflict threatens Key Internet Cables. Maritime attacks complicate repairs on underwater cables that carry the world’s web traffic.
Red Sea conflict threatens Key Internet Cables. Maritime attacks complicate repairs on underwater cables that carry the world’s web traffic.

Red Sea conflict threatens Key Internet Cables. Maritime attacks complicate repairs on underwater cables that carry the world’s web traffic.

Red Sea conflict threatens Key Internet Cables. Maritime attacks complicate repairs on underwater cables that carry the world’s web traffic.









Experience the flexibility, reliability, and security yourself

