In March 2020, NJFX founder and CEO Gil Santaliz, was in São Paulo for Capacity Latam. It was shortly before flights were grounded by the pandemic – a move that would force him to leave the show early – but that’s not the point of his story. As luck would have it, while Santaliz was out of the country, he received a phone call to say Chile’s Ministry of Transport and Communications (MTT) was visiting the US and wanted to tour NJFX.
“They wanted to get better insight into how cables operated in the US going to Europe, as well as going down to South America,” says Santaliz via video call from New Jersey.
In his absence, business development manager Sarah Kurtz hosted the delegates, alongside industry heavyweights from Tata Communications and Aqua Comms. But this was no run-of-the-mill tour. The visiting party included Natalia López, the head of the Telecommunications Development Fund division for the government of Chile and lead on the Asia-South America Digital Gateway Project.
López and the team didn’t just want to look at NJFX; the delegation wanted to understand the role of an integrated, colocation cable landing station (CLS) in creating a connectivity a gateway.
“Three years ago, the Undersecretariat of Telecommunications in Chile decided to move forward to make Chile a digital hub,” López explains.
“In order to reach that, we are deploying more than 15,000 kms of optical fibre for high-capacity domestic networks. This deployment will allow all localities to have access to a fibre-optic connection, doubling the current backbone capacity of data transmission for those areas. Alongside of that, we have worked strongly to enhance international connectivity,” López continues.
The two-part plan saw a sharp increase in the number of international interconnection points with neighbouring countries, achieved by developing fibre over 12 new border crossings, and then the first fibre route to link South America directly with Asia.
In progress
Due to the impending Covid lockdowns the party had to leave NJFX early, meaning Santaliz didn’t get to meet López in person; however, the knowledge share continued over the ensuing months and the Asia-South America Digital Gateway Project is moving at pace.
“We haven’t travelled since, nor have they, but we had the communication with the ministry from Chile and they are moving forward with their project,” Santaliz explains.
The digital gateway was announced in 2019 when MTT and the development bank of Latin America, CAF, signed a $3 million technical cooperation agreement to finance feasibility studies, later conducted by Subsecretaría de Comunicaciones (SUBTEL), Chile’s telecom regulator. The initial aim was to lay a cable up to 15,000 miles long with at least two fibre pairs and a transmission capacity of 10-20 Tbp.
“With these developments, Chile’s international bandwidth capacity will undergo a 40-fold increment,” López says.
The Transoceanic Cable was confirmed in July 2020 and officially named Humboldt by the regulator in January this year – with a route that would link Valparaiso, Chile with New Zealand and Sydney. According to the Chilean government it was the most cost-effective route, although Shanghai was originally being considered before international concerns were raised.
That aside, Santaliz says: “They are moving on their efforts to have Chile become the gateway towards, in this case Australia and from there on to Asia, basically. So Chile is the first country in Latin America creating this new gateway across to Sydney.”
López adds: “Currently, as there aren’t any direct routes to Asia Pacific, traffic from South America goes through the US. That directly impacts the latency and quality of service which is critical for new technology requirements such as 5G or IoT.
“We expect Humboldt will reduce the latency between the continents significantly, it will increase South America’s available capacity, it will provide diversity to existing regional routes that rely strongly on the US, and it will offer an alternative route to traditional Trans-Pacific systems.”
Over 2020 a series of further announcements emerged from the country. On the data centre front, EdgeConneX opened the first of two facilities in Santiago, and Huawei announced its second hub in the country would open in the same city by the end of the year.
Google’s 10,500km Curie cable landed in the coastal city of Valparaiso and phase two of the Caribbean Express cable was announced, connecting Panama to Chile, then linking into Ecuador and Peru.
Accenture calculates that in 2018 the digital economy accounted for 22% of Chile’s GDP and, as it will in other nations, 5G will drive that figure even higher in the coming years.
It’s a priority area for López and the departments she works with, and there’s much work ahead to secure the opportunity.
“Moving forward with the main objective, we have worked hard to lead the development of 5G networks in our region by being the first country to make spectrum available for 5G networks,” she says.
“In a context marked by the pandemic, with economic slowdown and drop in investments throughout the region, the Chilean telecommunications sector is expected to support the national economic recovery effort,” she continues. According to her figures, telecoms will bring more than $3 billion in investments through new projects and will create 60,000 new jobs, “which will play an important role for the country’s economic recovery in the coming years”.
“In addition, various reports indicate that 5G will generate an economic impact of 1% of GDP by 2035, as long as we are innovative to work on creating value. This 5G digital infrastructure is what will allow Chile to compete in the 4.0 digital economy of AI and the Internet of Things,” says López (pictured below).
Independent LatAm
On that point, the knowledge exchange with NJFX has covered a number of topics.
“We have shared with them the concept of being open, the benefits of having a landing station used for multiple cables, not just one at a time,” Santaliz explains.
“We gave our advice to them and they are reviewing it and we have conversations on their architecture. Depending on the final grouping they have, the members of this new cable, we might even be able to develop their landing station for them. So that’s an opportunity that we would consider, depending on who the anchor consortium members would be for that,” he adds.
Developing a CLS takes up to two years, by which time Chile’s requirements will have progressed significantly, but the country – and wider region – are well ahead in preparing for future needs.
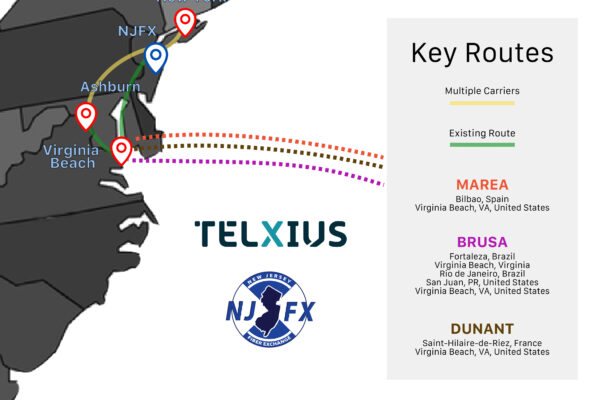
“There’s an incredible amount of investment already happening in South America,” says Santaliz, citing the Monet, BRUSA and Seabras-1 cables.
“They are going to start going through the end-of-life cycle with the existing cables that are there and one of the challenges is to make sure that the new cables – even though they have so much greater capacity than the old cables – you’re going to still need more of them,” he adds, before revealing that, “we should expect two more cables announced within the next two years.”
However, this next generation of cables – such as Ellalink, connecting Lat Am to the US, and the South Atlantic Cable System linking Angola with Brazil – will not depend on the US. It’s a trend Santaliz says is bringing independence to the region, but it needs to extend beyond the shoreline – and that’s a subject he is so passionate about, he featured on this year’s day three Capacity Latam panel, Delivering diverse connectivity to Latin America.
“The last challenge is you have the arteries built but do you have the capillarity in place? Is there going to be a competitive landscape for capillarity in Lat Am? Because inexpensive international capacity doesn’t give you very much if you don’t have competitive local access. The ministry is very aware that it is not about landing a cable – how do we get that cable’s connectivity across the country?
“So that’s the next challenge you’re going to have to develop – getting that infrastructure built,” Santaliz adds. While he’s a fan of the public-private model championed by the US for its rural connectivity needs, he sees another, equally transferable model, gaining popularity.
“What you are seeing is partnerships that we have not seen before.”
Giving an example, he explains: “The MVNOs… In the US if you have Verizon making the investment, they are going to allow Comcast, they are going to allow Altice, AT&T to piggyback on the deployment of their 5G. So you are going to see multiple partners that are non-traditional, starting to work together, to make the economics of 5G work in the US.”
In short, it’s all about “understanding what the private sector’s costs are in deploying private infrastructure”.
No doubt such trends will wash up on Chile’s shore, but for now the focus is on the plan in motion.
“To sum up, we can say that Humboldt cable is part of a very ambitious plan of the government of Chile to promote the essential digital infrastructure to become a key player in the digital economy and becoming a hub in our region,” López concludes.
###
About NJFX:
NJFX is a Tier 3 Carrier Neutral Cable Landing Station campus. Our colocation ecosystem has expanded to over 35 network operators offering flexibility, reliability, and security. Our Wall, NJ location provides direct access to multiple subsea cable systems giving our carriers diverse connectivity solutions and offers direct interconnection without recurring cross-connect fees.